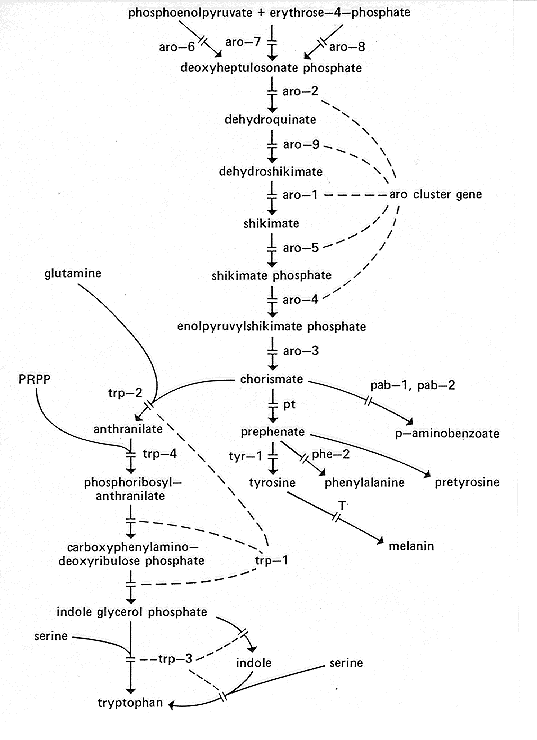
FIG. 11. Biosynthetic pathways of the aromatic amino acids, showing
sites of action to the aro, trp, pt, phe, tyr, and T genes (98, 147, 201,
259, 316, 387, 437, 473, 519, 546, 1126, 1167). The conversion of
chorismate to p-aminobenzoate has not been demonstrated in
Neurospora. In the conversion of tyrosine to melanin, the later steps
are nonenzymatic. The gene products of trp-1 and trp-2 form an
enzyme aggregate with three properties; a given trp-1 mutation may
block one or more of the reactions. aro-9+ activity (biosynthetic
dehydroquinase) can be replaced by the product of qa-2+, the
equivalent gene in the catabolic pathway (885). Pretyrosine accumulates
when other pathways are blocked (see phe-2). PRPP, 5-Phosphoribosyl
pyrophosphate.
