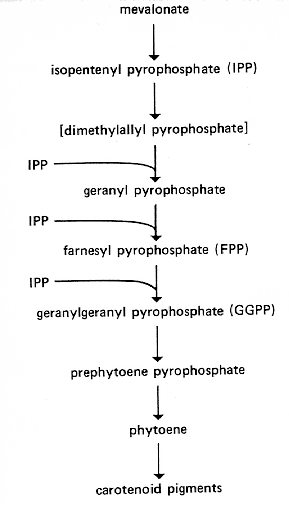
FIG. 9. Biosynthetic pathway for carotenoids. It is thought that the same prenyl transferase catalyzes all the steps from dimethylallyl pyrophosphate to geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (444; R.W. Harding, personal communication), and it has been proposed that a separate prenyl transferase converts dimethylallyl pyrophosphate to farnesyl pyrophosphate for sterol synthesis (445). The conversion of phytoene to the various carotenoid pigments involves a series of dehydrogenations, cyclizations, and other reactions. There must also be a cis/trans isomerization analogous to that found in tomato (842). The sequence of some of these steps is still uncertain; the pathway must branch, and there may be alternate routes to some of the products. See references 228, 443, 444, 842 and citations therein for proposed sequences. al-1 is probably blocked in phytoene dehydrogenase (398). It is not known whether this enzyme catalyzes the whole series of dehydrogenations. al-2 is reported blocked between geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate and phytoene (445) and between prephytoene pyrophosphate and phytoene (572). al-3 is alternately reported blocked between isopentenyl pyrophosphate and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (445) and between prephytoene pyrophosphate and phytoene (572), but it is not blocked in the production of farnesyl pyrophosphate or sterols (398, 445). ylo-1 is evidently blocked in a late step, probably either in the conversion of lycopene to 3,4-dehydrolycopene or in the conversion of either torulene or gamma-carotene to neurosporaxanthin (see citations in reference 398).