Strains for studying Spore killer elements in four Neurospora species
B.C. Turner and D.D. Perkins - Department of Biological Sciences, Stanford
University,
Stanford CA 94305-5020
This note gives a comprehensive list of stocks useful for working with Spore killer
elements, including reference strains for use as testers, genetically marked derivatives,
and
strains sensitive and resistant to killing by Sk-1K, Sk-2K, and Sk-3K. Geographical site
of
origin is indicted for the various killer alleles. Many of the strains are newly deposited
in
FGSC. Some are listed also under other categories. Updated versions of the list will
appear in future FGSC Stock Lists (Part IV, Special Purpose Stocks).
Characteristics of chromosomally located Spore killer elements have been
summarized by Turner et al. (Am. Nat. 137:416-429, 1991; Fungal Genet. Newsl.
34:59-62,
1987) and will only be summarized briefly here. In crosses heterozygous for killer and
sensitive (SkK x SkS), four ascospores are usually killed in each 8-spored ascus and the
survivors are SkK. All eight ascospores survive in crosses homozygous for the same
killer
element. Killer elements have been found in natural populations of N. intermedia
(Sk-2K
and Sk-3K, both rare) and N. sitophila (Sk-1K, common). Sk-2K and Sk-3K have been
introgressed from N. intermedia into N. crassa for convenience of genetic analysis. Both
are
haplotypes-presumed gene complexes in a centromere-spanning segment of linkage group
III within which meiotic recombination is repressed in the killer/sensitive heterozygotes.
Sk-2K and Sk-3K are similar in behavior except that each is sensitive to killing by the
other.
The two also differ in their reaction to genes conferring resistance to killing. Genes
conferring resistance to Sk-2K or to Sk-3K are present in some populations of N.
intermedia.
Resistance to Sk-2K is found at low frequency throughout the range of N. crassa. The
resistance genes, symbolized r(Sk)-2 and r(Sk)-3, have been mapped in wild type sequence in
N.
crassa. They are linked to loci within the killer complex. Map relations in N. crassa are
shown in Figure 1. Linkage relations of Sk-1K are not known, nor is it known whether
this
killer element is associated with a complex.
Sk-2K strains have been found only in N. intermedia, and only in four localities:
Brunei (B), Java (J), Papua New Guinea (P), and Sabah (SA). Sk-3K is known solely
from
Papua New Guinea. All commonly used N. crassa laboratory wild-type strains and their
derivatives are sensitive to killing both by Sk-2K and by Sk-3K.
Strains containing the aconidiate mutation fluffy (fl) are conveniently used a female
parents in test crosses for scoring killer vs. sensitive. The fl testers are highly fertile, and
because conidia are absent, ascospores ejected to the sides of the tube can be seen
clearly.
With N. crassa, tests are made by fertilizing the testers on 10 x 75 mm slants of synthetic
cross medium with 1% sucrose and examining shot ascospores after 10 days at 25 C.
With
N. intermedia, N. sitophila, and N. discreta, tests are best made on 13 x 100 mm slants
using
synthetic cross medium with filter paper as sole carbon source. If this medium is
employed,
stocks without the fluffy mutation can be used, because few conidia are produced.
Standard
stocks of N. tetrasperma are also satisfactory as testers because they make few conidia at
25 C, even on sucrose medium.
Table 1. Strains for identification and study of Spore-killers in
Neurospora
Species and Origin of FGSC No. Comment
genotype allele* A a
Neurospora crassa
Sk-2K B 6648 6647 10th backcross to N.
crassa, mixed background
Sk-2K B 3114 3115 10th backcross to N.
crassa, inbred to OR wild type
cum Sk-2K acr-7 B - 7432
Sk-2K acr-7 B 6930 - 10th backcross to N. crassa
Sk-2K acr-7 leu-1 his-7 B - 7373
Sk-2K acr-2 leu-1 his-7 B 7387 7388
Sk-2K acr-2 leu-1 B 7375 7374
Sk-2K acr-2 his-7 B 7376 7377
Sk-2K leu-1 B 7371
Sk-2K his-7 B 7378
Sk-2K phe-2 dow B 4538 4539
Sk-2K dow B 4260 4261
Sk-2K; fl B 3297 3298 9th backcross to N. crassa
Sk-2K P 7368 7367 12th backcross to N. crassa
Sk-2K acr-2 P 7385 7386
Sk-2K J 7369 7370 12th backcross to N. crassa
cum Sk-2K acr-2 J 7383 7384
Sk-2K acr-2 J 6928 6929 15th backcross to N. crassa
Sk-2K J 7392 7393 Used for testing N. crassa
from India
Sk-2S Sk-3S fl@ 6682 6683 flP (RL) testers
r(Sk-2)-1 - 2222 - Iowa-1, LA (P527)
r(Sk-2)-1 cum - 7379 7380
cum r(Sk-2)-1 acr-7 - 7389
r(Sk-2)-2 - 7398 Derived from N. crassa
P2604, Georgetown, Malaya
Sk-3K P 3577 3578 10th backcross to N. crassa
cum Sk-3K P 7382 7381
cum Sk-3K his-7 P 7390 7391
Sk-3K acr-2 P - 7077
Sk-3K acr-7 P 6931 6932 15th backcross to N. crassa
Sk-3K fl P 3579 3580 10th backcross to N. crassa
Sk-2K Sk-3S fl@ 6682 6683 flP (RL) testers
r(Sk-3) 7395 - 6th backcross to N. crassa
cum r(Sk-3) - 7396 6th backcross to N. crassa
cum r(Sk-3) leu-1 - 7394 9th backcross to N. crassa
r(Sk-3) acr-7 ser-1 7397 - 6th backcross to N. crassa
Neurospora intermedia
Sk-2K B 7401 7402 3rd and 4th backcross to
Taipei background
Sk-2K P 7429 - 3rd backcross to Taipei
background
Sk-2K J 7399 7400 f1 of Tjiawi-2d (P162)
x Taipei-1c (P13)
Sk-2K SA 7426 - Menggatal, Sabah (P3126)
r(Sk-2) 1832 1833 Townsville-1b (P113),
Townsville-1 (P112)
Sk-3K P 3193 3194 Derived from Rouna-1 (P32)
r(Sk-3) 6595 5123 Tahiti (P2427, P2421)
Sk-2S Sk-3S@ 3416 3417 Shew wild types (Taipei
background)
Sk-2S Sk-3S fl@ 5798 5799 7th backcross of flP from
N. crassa to Shew wild types
Species and Origin of FGSC No. Comment
genotype allele* A a
Neurospora sitophila
Sk-1K 2216 2217 Derived from Dodge's Arlington
stocks
Sk-1K; fl 4762 4763 fl P(1012) from Whitehouse N.
sitophila, 3rd backcross to Dodge
stocks
Sk-1S 5940 5941 Tahiti (P2443, P2444)
Sk-1S; fl 4887 4888 5th backcross of flP from N. crassa
to Panama VP203 or derivative
Neurospora tetrasperma
(See Raju and Perkins 1991 Genetics 129: 25-37. E: 8-spored ascus.)
Sk-2K acr-2 J 6934 6935 8th-9th backcross to N. tetrasperma
Sk-2K acr-2; E J 6936 6937 4th backcross to N. tetrasperma
Sk-3K acr-7 P 6938 6939 7th-8th backcross to N. tetrasperma
Sk-3K acr-7; E P 6940 6941 8th backcross to N. tetrasperma
Sk-2S 1270 1271 Wild types 85A, 85a (also Sk-3S)
Sk-2S; E 5897 5901 85A, 85a background (also Sk-3S)
* B: Brunei (Borneo); J: Java; P: Papua New Guinea; SA:
Sabah (Borneo).
"nth backcross" Indicates progeny from the nth backcross of SkK
into the alien genetic
background. Introgressed killer strains with markers, for which
there is no comment, are
all from well backcrossed parents. Stock numbers prefixed with P
are given for strains that
originated from nature. For origins of stocks designated by place
names, see FGSC
Neurospora Stock List, Part V.
@ These strains are sensitive to killing both by Sk-2K and by
Sk-3K. The double symbol is
used to specify phenotype, and does not imply that Sk-2K and Sk-3K
necessarily represent
two genes at separate loci. It has not been determined how many
loci are involved in
determining sensitivity vs. resistance to either or both Spore
killers.
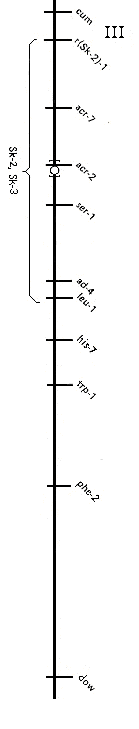
Figure 1. Loci of linkage group III that are relevant to Sk-2 and Sk-3. Meiotic crossing
over in the region
between acr-7 and leu-1 is normally about 30%. Crossing over in the acr-7 - leu-1
interval is effectively abolished
in crosses where one parent contains Sk-2K or Sk-3K and the other is sensitive or
contains a gene conferring
resistance. r(Sk-3)-1 is located near r(Sk-2)-1. r(Sk-2)-2 has been mapped close to
leu-1.
